
Nightingale attempted unsuccessfully to have the census modified to make it a more effective source of data for public policy.
#Who was florence nightingale code
Jocelyn Keith described the proposal as “the first model for the systematic collection of hospital data using a uniform classification of diseases and operations that was to form the basis of the ICD code used today.” 3 Nightingale sent a proposal for improved statistics of surgical operations to the International Statistical Congress held at Berlin in 1863, which took the analysis a step further. 2 The delegates took up her proposal, adopted a resolution to that effect, and forms were duly drawn up.
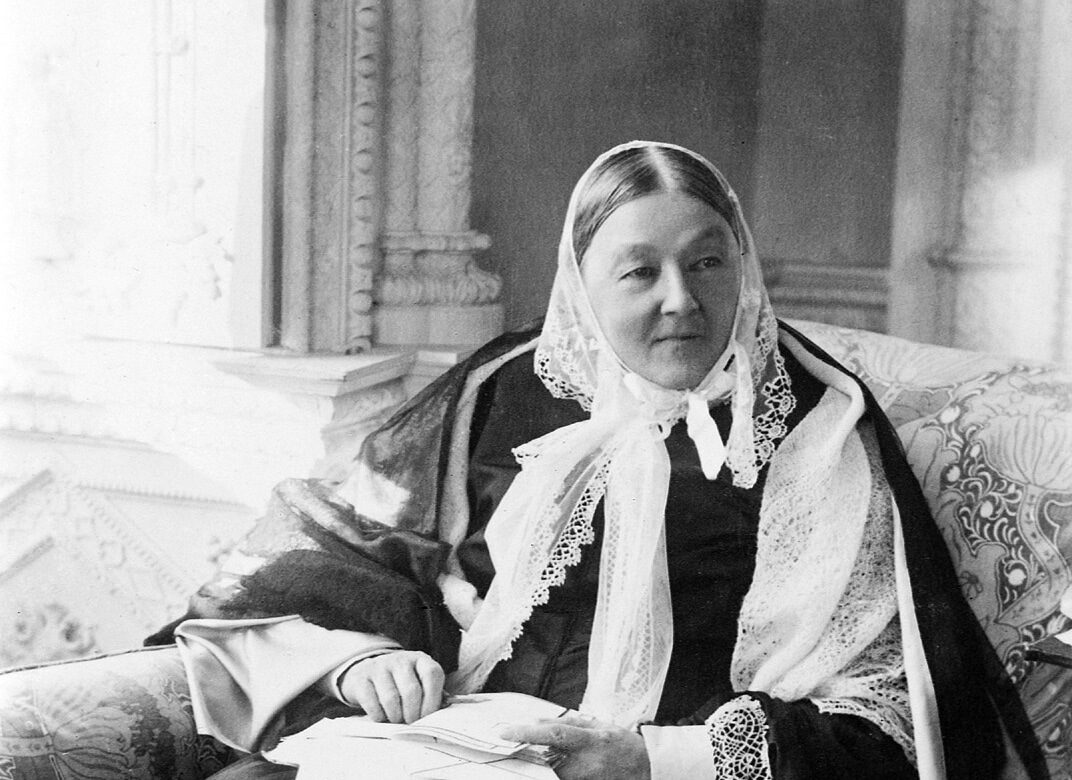

She sent a letter advocating the uniform collection of hospital statistics, so that outcomes could be compared by hospital, region, and country. Nightingale found another opportunity to achieve reforms during the 1860 International Statistical Congress, which was held in London and presided over by the eminent Belgian statistician, Adolphe Quetelet. 1 One recommendation was for the creation of a statistical department to track rates of disease and mortality and to identify problems so that they could be dealt with promptly. The royal commission report that was eventually produced showed Nightingale's work from its conception, terms of reference, choice of members, and analysis of data to its recommendations for change. She worked with a team of “sanitary experts,” including William Farr, who was Britain's leading social statistician at the time. She pressed for the creation of a royal commission to investigate the causes of the high mortality (eg, for every 1 soldier that died from his wounds, 7 died from disease). Nightingale returned from the Crimean War with a conviction that the desperate loss of life she witnessed should never occur again. Nightingale was keen not only to get the science right but also to make it comprehensible to lay people, especially the politicians and senior civil servants who made and administered the laws. At a time when research reports were only beginning to include tables, Nightingale was using bar and pie charts, which were colour coded to highlight key points (eg, high mortality rates under certain conditions). She was also a pioneer in the graphical presentation of data. She herself was a pioneer developer of survey instruments, always vetted by other experts and pretested on appropriate cases. Nightingale's leadership style was very much knowledge based. For Nightingale, this entailed the best possible research, access to the best available government statistics and expertise, and the collection of new material where the existing stock was inadequate. For more information visit .uk .Let's begin by looking at Nightingale as a systemic thinker and a “passionate statistician.” Her work in nursing and social reform was informed by a religious faith or philosophy that favoured a systemic approach: God made the world and runs it by laws, which we can discover by research in both the biophysical and social spheres.

The Florence Nightingale Museum is housed in Guys and St Thomas Hospital, on the site of the original Nightingale Training School. She would be proud, as we all are of all of the healthcare workers who are working on the front line to treat patients, fight the infection and reduce casualties.” “The whole of the country is practicing methods taught by Florence Nightingale. Both are in the exhibition, as is a recording of her voice, made in 1890.ĭavid Green is in no doubt about Nightingale’s legacy. More recently, the museum has worked with Mattel to create a Florence Nightingale Barbie doll. Between 19, she was the face of the £10 banknote. It would, eventually, catch up with her, but she worked to the end.įlorence Nightingale died in 1910, at the age of 90. Fever, insomnia, exhaustion and depression, all were ignored in her one-woman quest to reform public health care. “She probably had PTSD,” says David Green. In 1858 she became the first woman admitted to the Royal Statistical Society and she would later become an honorary member of the American Statistical Association.Īll the while, Nightingale was suffering herself. “She wrote 14,000 letters to members of the establishment and to get their attention she needed to make her points short and pithy”.

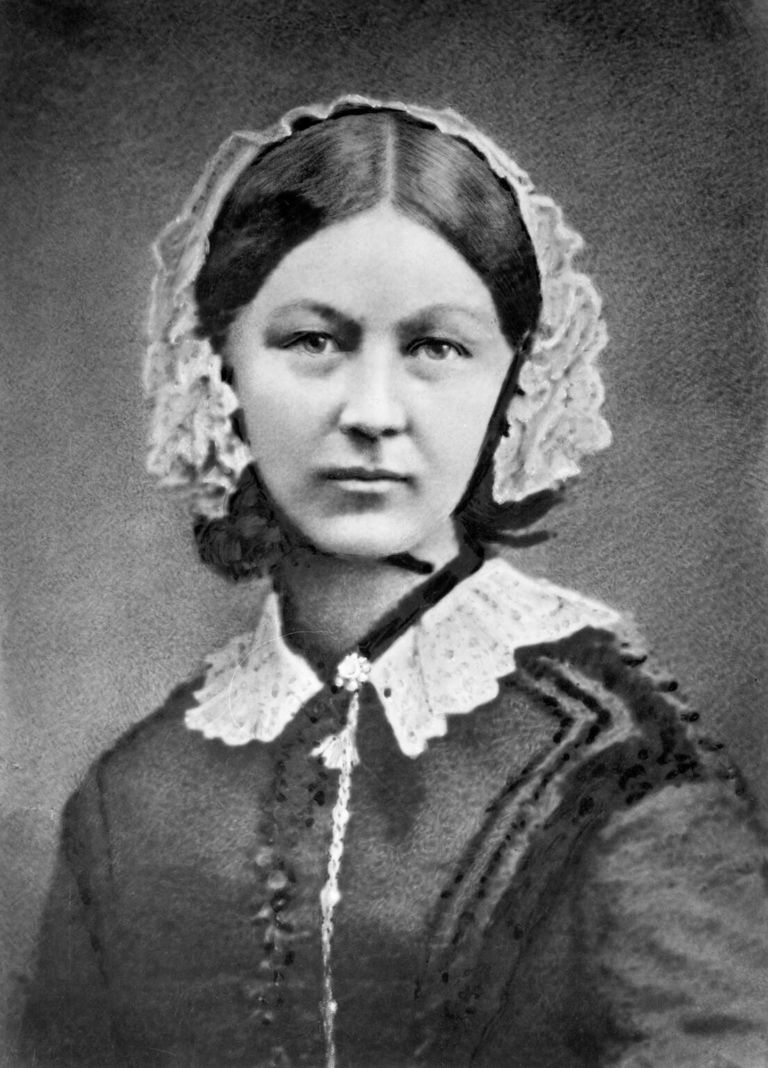
“She knew the power of infographics,” says David Green. This is not true, but she was a pioneer in using data in her campaigns for social reform. There is an urban myth that Florence Nightingale invented the pie-chart.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
